Apache Jmeter Download For Mac
This article illustrates how to use the Shell Script Automation Host Feature to pull tests from GitHub, run tests from the command line on a .jmx file, parse the results, and automatically upload the test results to qTest Manager.
After the initial upload, the script allows you to schedule specific tests from qTest Manager, rerun tests, and update only those results on qTest.
JMeter is a 100% Java application and should run correctly on any system that has a compliant Java implementation. JMeter has been tested and works under: You can update this page to add your systems. For JMeter 2.12 (Java 6+) (OS alphabetical order). Download Apache JMeter. We recommend you use a mirror to download our release builds, but you must verify the integrity of the downloaded files using signatures downloaded from our main distribution directories. Recent releases (48 hours) may not yet be available from all the mirrors. In order to guard against corrupted downloads/installations, it is highly recommended to verify the signature of the release bundles against the public KEYS used by the Apache Maven developers.
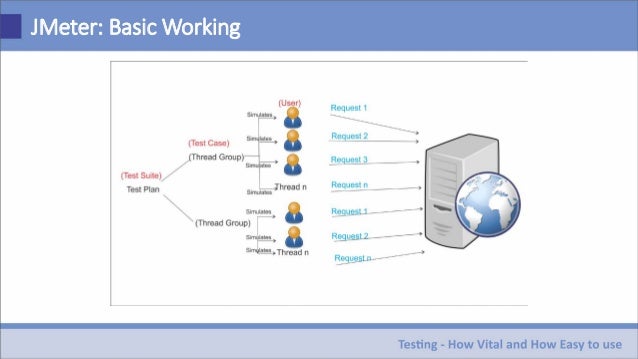
What is Apache JMeter? Apache JMeter is an Apache project that can be used as a load testing tool for analyzing and measuring the performance of a variety of services, with a focus on web applications. Steps to Download and Install Jmeter in MacOS: Pre-requisite: Install and download the latest JRE and JDK in your local machine. Apache JMeter is an Apache project that can be used as a load testing tool for analyzing and measuring the performance of a variety of services, with a focus on web applications (Wikipedia).
Prerequisites
You will need to install the following applications to use the JMeter Automation Feature:
Python 3.6 from https://www.python.org/downloads/
PIP (package manager for Python)
Apache JMeter from https://jmeter.apache.org/download_jmeter.cgi
Git for the Command Line from https://git-scm.com/download/

Tips for Prerequisite Set Up
Check PIP Installation
These instructions will work from Terminal (Mac) or Command Prompt (Windows).
Run this command to ensure the PIP install with Python was successful. It should output the pip version:
If PIP did not install, run the command below:
For more information on PIP installation, read here:Once the PIP install is successful, run the following commands individually:
These commands will install the necessary modules required to run the Python scripts. The modules are used to send requests to the API, read JSON configuration files, parse .xml documents, and upload files to qTest.
Windows
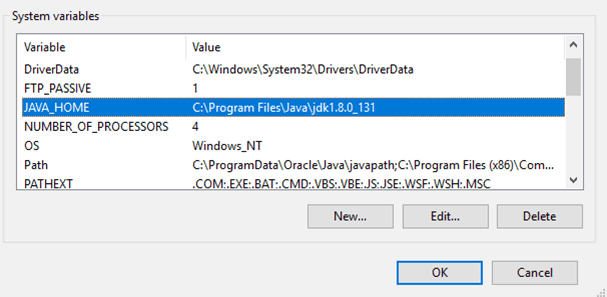
Ensure that all environment variables are set up correctly, before running the Automation Host script, specifically that the PATH variable is updated for Python, JMeter, and Git.
Mac
Use Homebrew to install Python and Maven. Steps for installing Homebrew can be found at https://brew.sh
Once you install Homebrew, run the following command to get Python 3:
Enter the following command to get Apache JMeter:
JMeterAutomation Host Example from GitHub

Update Configuration File
Open the conf.json file, and update with your personal information. Enter your own qTest URL and API Token found in your qTest Manager Environment.
git_url: The shell script uses the URL to clone a repository and send pull requests every time it runs if -git input is used.
local_repository: The folder containing the .jmx file. The shell script will use this to know where to run the tests.
qtest_api_token: The token used to authorize the connection to qTest Manager.
qtest_url: The personal URL that is used to access the qTest API.
Jmeter Apache Download
Setup Automation
Follow these instructions to set up your automated testing:
Access qTest Automation Host.
For information on accessing qTest Automation Host, refer to Access qTest Automation Host for Windows, Access qTest Automation Host for Mac, or Access qTest Automation Host for Linux.Click the Add button in the Agents section to add a new agent.
In the New Agent window, enter the appropriate information for the following fields:
General Agent Information
Agent Name: Name
qTest Manager Project: Select your project
Agent Type: Choose Shell Agent
- Test Scripts Information
Directory: The directory containing your scripts and shell agent (Directory where the scripts were cloned)
Allocated Execution Time: Amount of time you expect the script to take to execute in minutes
- Kick-off Scripts: The file path to your shell script. This shell script takes in two inputs, one for using git and the second for updating your current test cycle.
To give the shell script permission to run, use the following command:
Windows: run.bat
Linux: chmod +x run.sh
Shell Script Inputs:
-git
Uses GitHub to clone a test case repository and send pull requests every time the shell script is run.
-update
Updates an existing test cycle or create a new test cycle if the first test run.
(To create a new test cycle every time the script is run, do not use this argument.)
To run the shell agent, without using GitHub or updating the existing test cycle, do not include the parameters above in the Kick-off Scripts section.
Save to close.
Run the Shell Script
To start the shell script, select the yellow icon in the action field which will upload all of the test cases to qTest Manager.
Schedule your Tests
In Manager, select the Test Execution tab.
Locate the Test Cycle in your project named 'Jmeter Automated Tests'.
Select the Test Cycle and it will display all of the tests that were run through the maven build along with their statuses.
Select the check boxes for the specific tests you would like to schedule and select 'Schedule' from the 'More' drop-down menu.
In the Agent drop-down menu, select the Shell Agent and select OK.
Once the tests are scheduled, you will need to go back to the Automation Host and select Poll Now to kick the Shell Agent off.
Apache Jmeter 3.2 Free Download
Tips for .jmx File:
Apache Jmeter Download Windows
When setting up the Test Plan for JMeter, make sure to configure the aggregate report for each thread group to “Save as XML” as shown below. This configuration will create a results.xml that the parser will be able to read and upload results to qTest Manager.
